Arthrosis
Arthrosis or Osteoarthritis in medicine is the name of a condition on the cartilage in joints.
Osteoarthritis is also commonly called joint wear. Osteoarthritis occurs because more articular cartilage is lost than can be produced by the body. The cartilage deteriorates and sometimes it disappears completely. Due to wear of articular cartilage and a reduction of the shock-absorbing fluid in the joints, bones can rub over each other, causing a lot of pain. Osteoarthritis occurs mainly in the joints of the hands, knees, shoulders, neck and hips.

Complaints
Osteoarthritis is characterized by pain during movement of the affected joint and by a stiff or stiff feeling.
The joint is especially stiff after not moving for a while, for example in the morning. The basic joints of the thumb are often most affected in the hand. Due to the pain, the thumb is less used and the pigeon can languish (artify).
Osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear, overloading or due to previous injuries.
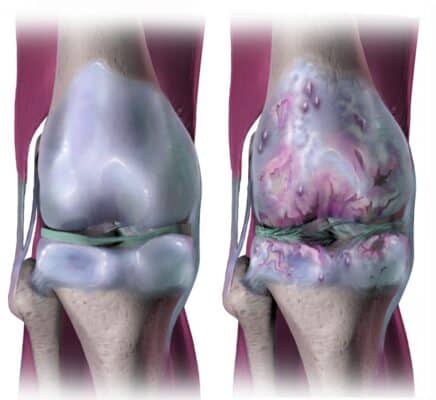
Cause
Osteoarthritis can actually be seen as a normal process of the joints as soon as there is a shortage of burden on the total cartilage surface.
Risk factors for the development of osteoarthritis are:
- Chronic overexertion or the wrong load in which people are quickly inclined to strain parts of the body, such as during physically demanding work or intensive exercise.
- Overweight plays an important role in osteoarthritis of knees, hips and ankles.
- Trauma in damaged joints, for example due to sports injuries, may also cause osteoarthritis.
- Heredity osteoarthritis occurs to a certain extent in everyone. In rare cases, early osteoarthritis is a disease that is dominantly inherited.
- Inflammatory reaction; osteoarthritis is also caused by a slight inflammatory reaction of the body. This inflammatory reaction accelerates the breakdown of articular cartilage.
Treatments
The conservative treatment of osteoarthritis has two main objectives, namely relieving pain and maintaining function. There is no cure for osteoarthritis. This does not mean that you can not do anything to alleviate the discomfort.
Movement and weight loss: Because overweight is an influenceable risk factor for osteoarthritis and it increases the load on the joint, it is strongly recommended to lose weight in case of overweight.
Operation: With a number of joints, it is now possible to replace a severely affected joint that causes a lot of pain with an artificial joint. This happens especially at the knee and the hip.
Medicines: Another form of conservative treatment of osteoarthritis consists of pain relief by means of medicines. Usually it starts with taking paracetamol. Vitamin D and Polyphene has a beneficial effect on the effects of osteoarthritis in overweight; it reduces the pain and movements are less disturbed.
View our solutionWhat exactly is Athrosis?
Arthrosis is a type of rheumatism in which the cartilage in the joint deteriorates in quality. It becomes thinner, softer and crumbly. This leads to deformation of the bone directly underneath the cartilage. There are visible and tactile nodules called osteophytes at the edge of your joint. These nodules limit the mobility of your joint.
Sometimes there is inflammation in the joint. Also nerves are sometimes pinched, causing pain, sensory disturbances and loss of strength. Arthrosis is the most common rheumatic disorder of the musculoskeletal system.
Arthosis is a condition that involves the entire joint and can occur in all joints. There are joints in which it occurs more frequently, such as in the neck, lower back, knees, hips, thumb, fingers and big toe. The condition is relatively common. The international name of Arthrosis is osteoarthritis.
How we can help you with Arthrosis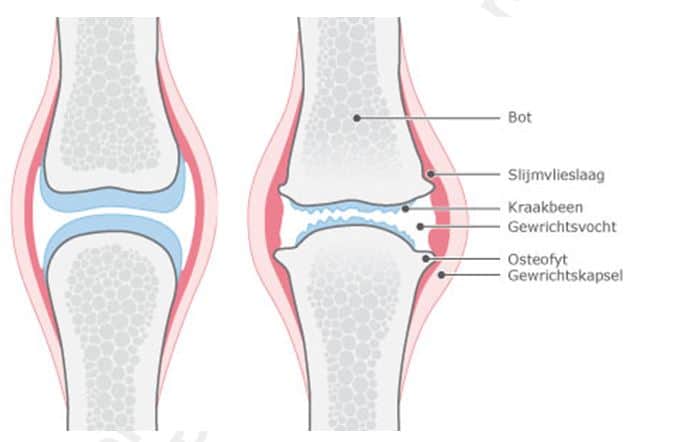
Diagnosing Arthrosis
Your doctor will usually base the diagnosis on the outcome of the complaints you indicate, the physical examination and the blood test. Your doctor will examine your joints if moisture is present and / or there are palpitations that can be felt. The doctor can also feel at your joint how much cartilage there is between the two joint parts. Your doctor will look further depending on your symptoms and the physical examination.
Blood test
Osteoarthritis can not be determined by blood tests. Your doctor often lets you take blood samples to rule out other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout or iron storage disease (hemochromatosis) as much as possible. If there are no abnormalities from blood tests, this can be a confirmation of the diagnosis of osteoarthritis.
Additional tests
In addition, your doctor often does additional tests. He has one or more x-rays taken to see if any abnormalities of your joints are visible. The information this produces is often limited. On the photo deviations can be seen, while you have few complaints or vice versa: the photo looks good, while you have a lot of pain.
How does Arthrosis progresses?
If there is a clear cause of osteoarthritis in a certain joint, chances are that it will stay with one joint. For example, if you have osteoarthritis due to damage to the meniscus in a knee joint, this does not automatically cause osteoarthritis in the other knee joint.
Is there no possible cause for your osteoarthritis to be identified? Then it is more likely that you get osteoarthritis in several joints.
Everyone has a different arthritis. Pain, stiffness and limitations of your joint are common complaints. Also the degree and speed in which your cartilage deteriorates is different for everyone. There are people who only have pain complaints at heavy loads. But there are also people who need a joint prosthesis because the cartilage and the underlying bone are too damaged. If the damage is great, you usually have a lot of pain and your joint is difficult to use.
Good for JOINTS
Good for JOINTS, with Magnesium, Manganese and enriched with natural Vitamin C, D3 and K2 for optimal effect. Contains Polyphine JOINTS, OPC en Hydroxytyrosol polyphenes from grapeseeds and olives harvested in France. Contains Glucosamine, MSM and Molybdenum
Order the intro pack

 Nederlands
Nederlands Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Italiano
Italiano Español
Español